Command
Command Type
There are three types of you can build in your extension.
View Command
As the name suggests, this command type creates a view in the Command Bar. The Alt app uses the React library for its user interface, and you can use the DOM API and Extension API inside the view command. To match the Alt app user interface, use the provided UI components.
import { useEffect } from 'react';import { _extension, UiList, UiListItem } from '@aldot/extension';
function Component() { const items: UiListItem[] = [ { value: 'hello-world', title: 'Hello World', onSelected() { _extension.ui.showToast({ title: 'Hello world', }); }, } ];
return ( <div style={{ padding: '1rem' }}> <UiList items={items} /> </div> );}
export default Component;View Command Action
Because the command view doesn’t have access to Node.JS API, you need to add an action for the command view. To add an action file, you only need to create a new file where the file name is the same as the view command but you must add the .action suffix for the action file. For example, search-files.tsx and the action file would be search-files.action.ts.
Directorysrc
- search-files.tsx
- search-files.action.ts
- manifest.ts
- package.JSON
- README.md
Inside the action file, you can only access the viewAction API.
Action Command
Opposite of the view command, the action type command doesn’t return view whatsoever. This command type runs in the background, and run in Node.js environment meaning that you access Node.js API.
import { _extension } from '@altdot/extension';
async function command() { await _extension.notifications.create({ title: 'Hello world', });}
export default command;Script Command
You can write the script command in any supported language, unlike the View and Action command type that can only written in JS or TS. And because of that, the script command doesn’t have access to the Extension API.
And because the script command is just a script that runs on the user’s computer, whether the script can be run depends on whether the language is installed. For example, when the extension has a Python script, but the user doesn’t have Python installed, the app will throw an error when the user tries to run the script command.
The script command can show the user interface to the Command Bar by outputting JSON view and hasView is true in the manifest. For example,
const jsonView = { view: { type: 'text', text: 'Hello world!', },};
console.log(JSON.stringify(jsonView));import json
print(json.dumps({ "view": { "type": "text", "text": "Hello world!" }}))Supported Languages
The script command supported languages:
- JavaScript (using Node)
- Python
- Bash
- PowerShell
Command Arguments
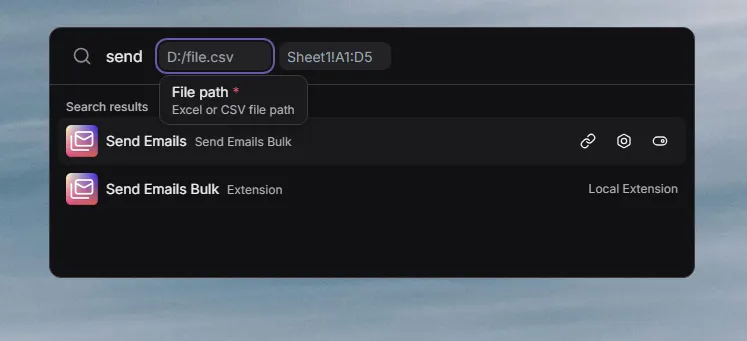
Arguments allow you to make the user pass values before running the command.
You can define the command arguments in the command properties of the extension manifest, and they can only have up to 4 arguments.
Accessing Arguments
view and action type
For view and action type commands, you can access the argument values in the args property of the function parameter.
import { CommandLaunchContext } from '@altdot/extension';
function Command({ args }: CommandLaunchContext<{ fileName: string }>) { console.log(args.fileName);}
export default Command;script type
For the script type command, the argument values can be accessed in the environment variable. The argument property name has a __ARGS__ prefix, and the argument name itself will converted into a SCREAMING_SNAKE_CASE. For example, when the argument name is file-name, it can be accessed using the __ARGS__FILE_NAME key.
console.log(process.env.__ARGS__FILE_NAME);import os
print(os.environ["__ARGS__FILE_NAME"])